5 steps to search online
Key takeaways
- Enter clear and specific keywords related to your query to get the most relevant results.
- Use quotation marks around phrases to search for exact matches.
- Review the first few results and summaries to quickly find the information you need.
1. Choose a search engine
Different web browsers have default search engines. Google and Bing are the most popular search engines.
If you use Google Chrome or Safari, Google is the default search engine. If you use Microsoft Edge, Bing is the default search engine.
If you want to know more about how search engines work, please read the How search engines work article.
2. Find the search bar
In your web browser, there are two places you can start the search:
URL bar is where you type a web address or URL.

Search box is located at the top centre of the homepage when you open a new tab on your browser.
3. Use simple keywords
4. Refine your search
Sometimes your first search attempt may not answer your question. In this case, you can refine your search by adding more details. For example:
- Time and date: 2024 or September 2024
- Location: Australia or Victoria or VIC
- Description: Use adjectives to specify the information. For example, if you are looking to buy a laptop, you might add keywords like affordable, lightweight, and gaming, depending on what you are looking for.
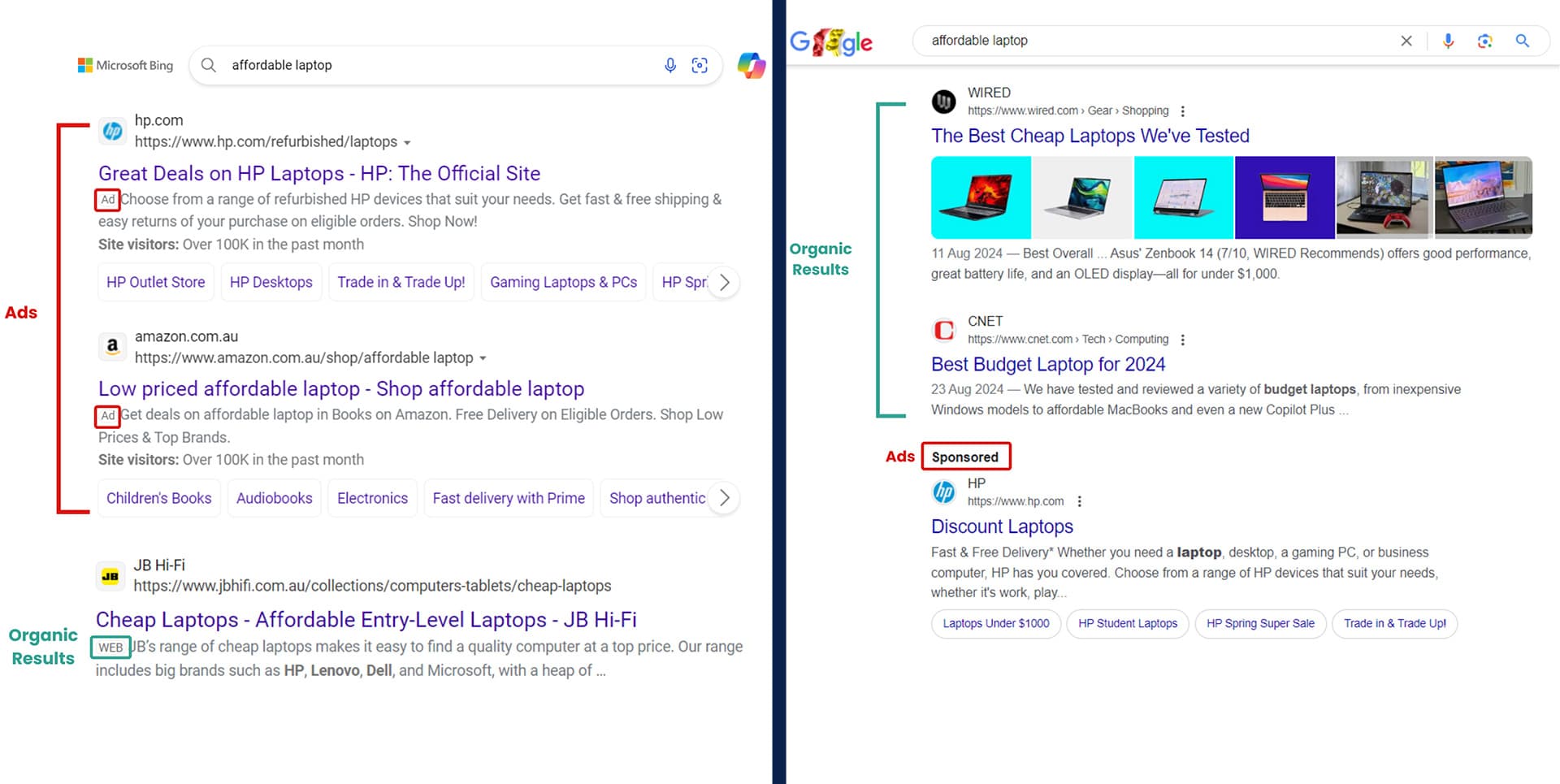
5. Understand search results
The search result page shows you both ads and organic results:
- Ads are often located at the top or bottom of the search result page. They are marked with a small label "Ad" or "Sponsored".
- Organic results are results that are not paid for. They are listed based on their relevance to your query.
It is also important to make sure the quality of the search results is good. You can consider:
- Relevance: Does the result answer your question or provide information for what you’re looking for?
- Authority: Can you trust the website? Sometimes, you can tell by checking the URL. This article includes information on how to read URLs.
- Timeliness: When was the content published? Is the information up to date?
- Navigation: Is the website easy to navigate? Can you find any grammar of text errors? A clear and user-friendly website sometimes indicates it is more professional and reliable.
Want to take your search powers even further?
Mastering Advanced Search Operators
Advanced search operators are powerful tools that can help you refine your search queries and find exactly what you’re looking for more efficiently. Here are some key operators and how to use them:
- Quotation Marks (“”): Use quotation marks to search for an exact phrase. For example, searching for
"climate change impact"will return results that include this exact phrase. - Minus Sign (-): Use the minus sign to exclude certain words from your search. For instance,
jaguar -carwill show results about the animal or the software, excluding those about the car. - Site:: Use the
site:operator to search within a specific website. For example,site:bbc.com climate changewill return results about climate change from the BBC website only. - Filetype:: Use the
filetype:operator to find specific types of files. For example,filetype:pdf climate changewill return PDF documents related to climate change. - Intitle:: Use the
intitle:operator to find pages with specific words in the title. For example,intitle:climate changewill return pages with “climate change” in the title.
By combining these operators, you can create highly specific search queries that save time and improve the relevance of your search results.
Glossary
- Web browser: An application you can use to access websites, such as Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge.
- Search engine: A website tool that helps you find information on the internet by typing in keywords. Examples include Google or Bing.
- URL: Stands for Uniform Resource Locator. It is the address of a specific web page.
- User-generated content: Original content created by users or customers.
- User interface:The design and layout of a webpage.
- Adjectives: Words you use to describe something.
Resources
GCF Global (How to search the web, Search suggestions, Refining your search, Content specific searches, Recognising ads)
End of article



